Acknowledgement: This article is also published on BarakB’s blog post
key Takeaways
- Text-to-Cypher converts natural language questions into executable Cypher queries against FalkorDB, streaming progress via Server-Sent Events
- Deploy the complete stack with one Docker command: FalkorDB database, web browser, REST API, and MCP server for AI assistant integration
- Connect Text-to-Cypher to VSCode or Claude Desktop through MCP, enabling graph queries directly within your development environment
We built something that lets you chat with your graph database in plain English. No more writing Cypher queries: just ask questions and get answers. We combined FalkorDB’s speed with a Text-to-Cypher translator and wrapped it all up with APIs you can actually use.
Everything’s open source. Check out the code on GitHub.
What We Built
FalkorDB stores and queries relationships between entities really fast. It speaks the Redis protocol, so you can use your existing Redis clients, and it uses Cypher for graph operations. If you know Redis, you already know how to connect to it.
Text-to-Cypher: Natural Language Interface
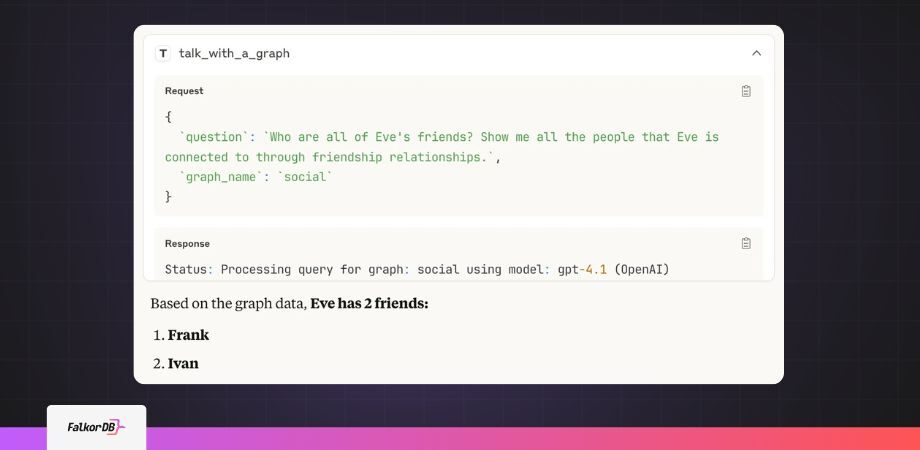
Text-to-Cypher connects to FalkorDB and translates your questions into Cypher queries. Instead of writing MATCH (p:Person)-[:FRIEND]->(f:Person) WHERE p.name = ‘Eve’ RETURN f.name, you just ask “Who are Eve’s friends?” and get back a readable answer.
There are two methods to use this new functionality:
- REST API: Call it directly from your apps. You get Server-Sent Events (SSE) that stream progress updates: schema discovery, query generation, execution, and results. Perfect when you want control and real-time feedback.
- Model Context Protocol (MCP) server: This exposes your graphs as resources that AI assistants can discover and query. Great for building multi-tool AI workflows where Text-to-Cypher works alongside other capabilities.
The REST API gives you tight integration with existing systems. The MCP server lets AI assistants and tools work together naturally. Pick what fits your architecture.
How It Works
Here’s what happens when you ask a question:
- You type a question in plain English (with optional conversation history for context)
- We fetch the graph schema from FalkorDB and cache it for speed
- AI generates a Cypher query based on your question and the schema
- FalkorDB executes the query and returns results
- You get an answer in English that actually makes sense
Getting Started
We packaged everything in Docker. One command gets you:
- FalkorDB Graph Database (port 6379)
- Graph Browser Web Interface (port 3000)
- Text-to-Cypher API (port 8080)
- MCP Server (port 3001)
docker run -p 6379:6379 -p 3000:3000 -p 8080:8080 -p 3001:3001 \
-v $(pwd)/.env:/app/.env:ro falkordb/text-to-cypher
Your .env file needs your AI model config:
- DEFAULT_MODEL=gpt-4
- DEFAULT_KEY=your-api-key-here
Load Sample Data
Let’s create a social network to play with. Here’s a bash script that builds a graph of people and friendships:
#!/usr/bin/env bash
GRAPH_NAME="social"
# Create nodes
redis-cli GRAPH.QUERY "$GRAPH_NAME" "CREATE
(p1:Person {name: 'Alice'}),
(p2:Person {name: 'Bob'}),
(p3:Person {name: 'Carol'}),
(p4:Person {name: 'David'}),
(p5:Person {name: 'Eve'}),
(p6:Person {name: 'Frank'}),
(p7:Person {name: 'Grace'}),
(p8:Person {name: 'Heidi'}),
(p9:Person {name: 'Ivan'}),
(p10:Person {name: 'Judy'})"
# Create relationships
redis-cli GRAPH.QUERY "$GRAPH_NAME" "MATCH (p1:Person {name: 'Alice'}), (p2:Person {name: 'Bob'}) CREATE (p1)-[:FRIEND]->(p2)"
redis-cli GRAPH.QUERY "$GRAPH_NAME" "MATCH (p2:Person {name: 'Bob'}), (p3:Person {name: 'Carol'}) CREATE (p2)-[:FRIEND]->(p3)"
# ... more relationships ...
redis-cli GRAPH.QUERY "$GRAPH_NAME" "MATCH (p3:Person {name: 'Carol'}), (p7:Person {name: 'Grace'}) CREATE (p3)-[:FRIEND]->(p7)"
This gives you a connected network great for testing natural language queries. You’ve got several options to query your graph:
- Web UI: Browse to http://localhost:3000 for visual exploration
- Text-to-Cypher API: Hit http://localhost:8080 with natural language queries
- OpenAPI Swagger UI: Try the API interactively at http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui/
- MCP Server: Connect your AI assistants on port 3001
Want to find Eve’s friends? Here’s how you’d ask:
curl -N --http2 -H "Accept:text/event-stream" -X 'POST' \
'http://localhost:8080/text_to_cypher' \
-H 'accept: text/event-stream' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"chat_request": {
"messages": [
{
"content": "name 3 of Eve friend",
"role": "user"
}
]
},
"graph_name": "social"
}'
You’ll see the Cypher query stream by, then the results, then a natural language answer. Pretty cool to watch it think.
The Underlying Tech Stack
OpenAPI: Making APIs Discoverable
You probably know OpenAPI already, but here we use it to let developers explore our API without reading docs. The Swagger UI generates itself from our OpenAPI spec, so you can test queries right in your browser.
MCP Server: AI Assistant Integration
MCP lets AI assistants discover and use your graph data. It handles:
- Listing available graphs and their schemas
- Exposing the text_to_cypher tool
- Streaming responses back via SSE
Connect with MCP Inspector to see it in action:
npx -y @modelcontextprotocol/inspector
The inspector aggregates all those streaming events into something readable.
Server-Sent Events: Real-time Feedback
SSE streams updates as we process your query. You see:
- Status messages as we work
- Schema discovery progress
- The generated Cypher query
- Query execution results
- Your final answer
This real-time feedback keeps users engaged, especially for complex queries that take a moment to process.
Integrating with Your Tools
VSCode Integration
Add Text-to-Cypher to VSCode by creating .vscode/mcp.json:
{
"servers": {
"talk_with_a_graph": {
"type": "sse",
"url": "http://localhost:3001/sse"
}
}
}
Now you can ask “using the information in the graph, list all Eve’s friends” right in VSCode. The model finds the right graph automatically through MCP resources.
Claude Desktop Integration
For Claude Desktop, add this to /Users/$USER/Library/Application Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json:
{
"mcpServers": {
"talk_with_a_graph": {
"command": "npx",
"args": [
"mcp-remote",
"http://localhost:3001/sse"
]
}
}
}
Note: Claude Desktop buffers SSE events rather than streaming them live.
What You Could Build
This opens up some interesting possibilities:
- Knowledge Base Queries: Let your team ask questions about your corporate knowledge graph
- Smart Customer Support: Give support agents natural language access to customer relationship data
- Research Tools: Help researchers explore complex datasets through conversation
- Enhanced Chatbots: Add graph-backed knowledge to your conversational AI
- Dynamic Analytics: Build dashboards that respond to natural language queries
Taking It Further
Think about building:
- Multi-source AI Assistants that combine graph data with other knowledge bases
- Data Lineage Tools that trace relationships through natural conversation
- Collaborative Analysis Platforms where teams discuss insights from shared graphs
- Domain-Specific Interfaces that understand your industry’s vocabulary
More can be found here, check out the code: https://github.com/FalkorDB/text-to-cypher
FAQ
How does Text-to-Cypher generate accurate Cypher queries?
It retrieves and caches your graph schema, then uses AI (GPT-4 or similar) to translate natural language into syntactically correct Cypher based on your actual data model.
Can I use Text-to-Cypher with existing FalkorDB instances?
Yes, Text-to-Cypher connects to any FalkorDB instance via Redis protocol. Configure the connection in your .env file with your database endpoint.
What's the difference between the REST API and MCP server interfaces?
REST API gives direct control with SSE progress updates. MCP server enables AI assistants to discover and query multiple graphs collaboratively.
Citations
- FalkorDB Text-to-Cypher Repository – github.com/FalkorDB/text-to-cypher – Open source implementation of natural language to Cypher translation with REST API and MCP server interfaces.
- Model Context Protocol (MCP) – modelcontextprotocol.io – Standardized protocol for AI assistant and tool interaction, enabling resource discovery and invocation.
- Redis Protocol Specification – redis.io/docs/reference/protocol-spec – Protocol documentation that FalkorDB implements for client compatibility.
- Cypher Query Language Reference – https://docs.falkordb.com/cypher/ – Comprehensive guide to the graph query language used by FalkorDB.
- Server-Sent Events (SSE) Standard – developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Server-sent_events – W3C standard for server-to-client streaming used for real-time query progress updates.