Workshop Recap: Building Knowledge Graphs with Graffiti
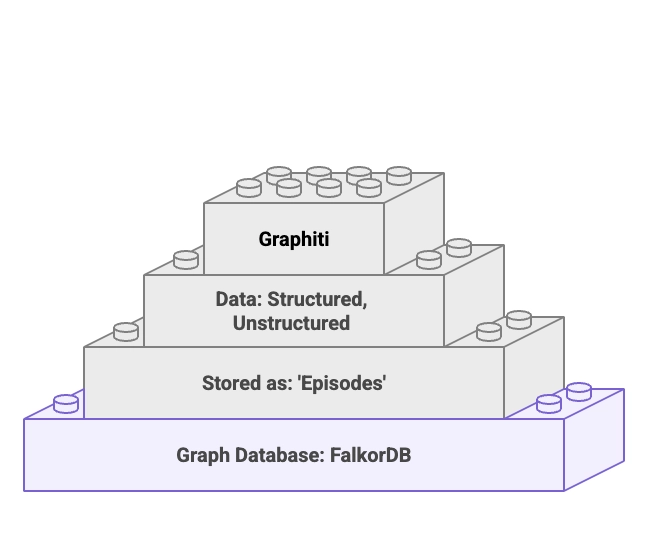
Graphiti is an open-source framework for building knowledge graphs that supports real-time, temporal data. It provides a structured approach for managing context, which is particularly relevant for LLM-based agents and advanced RAG pipelines. This article details Graphiti’s architecture and how it addresses limitations of traditional RAG by enabling agents to reason with state changes over time.
As Roi Lipman, co-founder of FalkorDB, notes, “A knowledge graph is just a way in which you can easily represent data. It is flexible, unlike relational databases.”
Graphiti and FalkorDB for GraphRAG
Graphiti works with graph databases like FalkorDB to store and manage its temporal knowledge graphs. This partnership provides a scalable foundation for graph traversal and data retrieval. By using FalkorDB, developers can build a graph that represents conversational history, user preferences, and other business logic. The architecture combines semantic search with graph traversal to retrieve context.
According to Daniel Chalef, founder of Zep, “Graphiti really provided a rich understanding of a broad and deep topic.”
Final Thoughts and Next Steps
Graphiti provides a robust way to manage context in dynamic environments. Its temporal-aware design and efficient retrieval mechanisms make it a viable solution for building sophisticated LLM agents and GraphRAG pipelines. The ability to reason with state changes is a capability that standard RAG systems lack, making Graphiti a valuable addition to an AI developer’s toolkit.
Review the Graphiti documentation and the FalkorDB GitHub repository to understand the implementation details. Run the provided examples to validate the approach for your own applications.
Citations & sources
[1] Chalef, D. (2024). Graphiti: The Open-Source Graph Framework. [https://zep.ai/blog/posts/introducing-graphiti]
[2] FalkorDB. (2024). FalkorDB Documentation. [https://docs.falkordb.com]
[3] Zep AI. (2024). Zep Is The New State of the Art In Agent Memory. [https://blog.getzep.com/state-of-the-art-agent-memory/]
[4] Zep AI. (2024). Graphiti Performance Benchmarks. [https://zep.ai/docs/graphiti/performance/]