Highlights
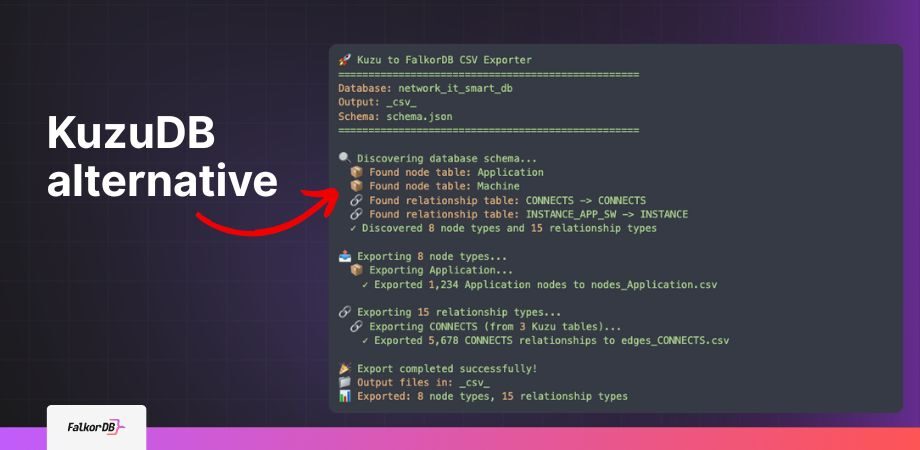
- You can run Kuzu to FalkorDB migration with auto schema discovery and CSV exports that preserve nodes, edges, properties, and metadata for a clean import path.
- You load exports with the FalkorDB Rust loader using async batching, streaming CSV, indexes, and constraints to feed GraphRAG pipelines with low latency reads.
- You keep Kuzu to FalkorDB migration repeatable in CI by verifying counts, tracking progress, and reading loader stats before switching traffic to the new graph.
KuzuDB archived its project and moved to read only status which signals an end to active support and maintenance for the codebase. FalkorDB offers a clear path for teams that need an actively maintained graph database with strong support for GraphRAG and agent centric workloads.
Context
KuzuDB publicly stated that it no longer actively supports the project and pointed the community to the archived GitHub repository, which now shows read only status after the archive event on Oct 10, 2025. The PyPI page also flags the archive and directs developers to the GitHub archive for continued access to prior releases and artifacts.
Kuzu delivered an embeddable property graph engine with a thoughtful storage and execution design that pushed performance for analytical graph workloads, and that contribution deserves real appreciation from everyone building graph backed systems. The published research and engineering around Kuzu influenced how many of us think about vectorized processing and graph analytics which will continue to carry forward in ongoing work across the ecosystem.
Why FalkorDB fits
FalkorDB focuses on low latency graph querying that feeds LLMs and GraphRAG pipelines which aligns well with applications that need reliable retrieval quality and fast agent loops. The project centers on practical developer workflows for building and serving knowledge graphs for AI and includes an active open source codebase and community presence.
Teams can follow a simple export then load approach that preserves nodes, relationships, properties, and graph semantics when moving graphs into FalkorDB based on documented migration patterns and reference projects. The general workflow mirrors other migrations into FalkorDB that rely on structured exports and programmatic loaders which keeps the process predictable and repeatable in CI and data jobs.
Pre-migration advice
Where to start
FAQ
What is the fastest way to do Kuzu to FalkorDB migration?
Export to CSV with schema discovery then load with the Rust loader which batches writes and streams CSV without loading entire files.
Does Kuzu to FalkorDB migration keep labels and relationship types?
Yes, the exporter writes node labels and edge types to CSV and the loader builds the graph then creates indexes and constraints.
References and citations
- FalkorDB Docs migration guide https://docs.falkordb.com/migration/
- RedisGraph EOL FalkorDB migration guide https://www.falkordb.com/blog/redisgraph-eol-migration-guide/
- FalkorDB GitHub organization https://github.com/FalkorDB
- Kuzu GitHub repository https://github.com/kuzudb/kuzu