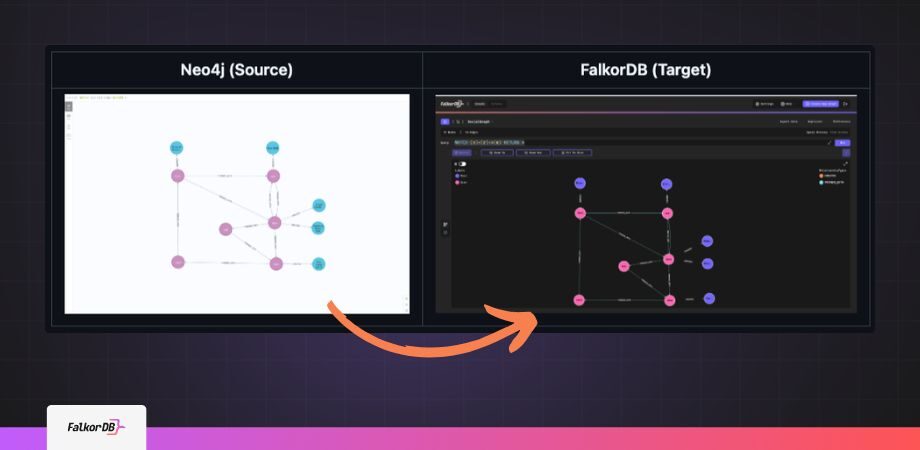
Highlights
- Neo4j to FalkorDB migration boosts query speed by 496x for real-time apps.
- FalkorDB’s OpenCypher support eases Neo4j migration with minimal code changes
- Multi-graph topology in FalkorDB ensures scalability and data isolation
A Guide to Migrating Your Graph from Neo4j to FalkorDB
Migration from one database to another may include data migration, adapting code and operational aspects. This guide includes a step by step walkthrough to migrate Neo4j data into FalkorDB. Whether your aim is to optimize performance, reduce costs, or leverage FalkorDB’s advanced multi-tenancy features, this guide will guide you through the steps to take in order to migrate effectively with minimal interruptions.
Graphs have become indispensable in various use cases, such as Fraud Detection, Cloud Security, Knowledge Graphs for GenAI and other workflows where accuracy and explainability are key. Among the leading technologies in this space are Neo4j and FalkorDB. While Neo4j is a well-established graph database with a variety of useful features and a mature ecosystem, FalkorDB offers a modern, lightweight, and an ultra-low latency alternative tailored for next-generation graph workloads.
What sets FalkorDB apart? Speed, scalability, and a seamless integration with GenAI pipelines. FalkorDB’s architecture natively supports both graph traversals and vector search, making it a natural choice for production-ready applications like Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), graph exploration, and knowledge representation in large-scale datasets.
In the latest set of performance benchmarks testing, FalkorDB shows significant performance advantages in aggregate expansion operations compared to Neo4j. The data reveals consistent 140ms response times at p99, while Neo4j experiences latencies exceeding 40 seconds under similar conditions.
High-Level Approach
Migrating your graph from Neo4j to FalkorDB is simple. Here are some key points to consider during the migration process:
- Setup FalkorDB: Before beginning the migration, set up your FalkorDB instance or cluster using Docker, or sign up to the FalkorDB Cloud.
- Export Data from Neo4j: Use python script to export nodes and edges CSV files, following an ontology specific mapping file. We’ll follow the guide also available on Github.
- Load the CSV data into FalkorDB: Load the CSV files using cypher commands as shown in https://github.com/FalkorDB/Neo4j-to-FalkorDB
- Compare and Verify the Migration: Finally, you can compare the Neo4j and FalkorDB graphs to ensure parity. Comparing the number of nodes and edges gives an indication.
- Visualize the Graph in FalkorDB (optional): Once the migration process is complete you can use FalkorDB Browser, a browser-based graph visualization tool, to visualize the graphs.
- Optimize FalkorDB for Production (optional): Finally, you can set up monitoring tools, configure cluster settings and implement backup strategies. On FalkorDB Cloud, these features are built-in, helping you scale and monitor easily.
Next, let’s go through an implementation of how to migrate from Neo4j to FalkorDB.
Steps to Migrate from Neo4j to FalkorDB
Before you begin, check the https://github.com/FalkorDB/Neo4j-to-FalkorDB GitHub repo, which can help you simplify your migration process.
Help us reach more developers, consider starring the repo!
For this guide, we assume you have installed neo4j and have access to it.
Step 1: Load the Movies dataset to neo4j
You can load the movies dataset by following the “:guide movies” command in the neo4j browser.
More details are available here: https://neo4j.com/docs/getting-started/appendix/example-data/
NOTE: if you prefer to use a different source dataset in neo4j, you can extract the existing ontology in the following step.
Step 2: Review Mapping config file and export CSV
Review the migrate_config.json file: https://github.com/FalkorDB-POCs/neo4j-2-falkordb/blob/main/migrate_config.json
You can use it to map labels, properties and edges. Here’s sample data for a movies dataset:
{
"label_mappings": {
"Person": "Person",
"Movie": "Movie"
},
"property_mappings": {
"Person": {
"name": "name",
"born": "birth_year"
},
"Movie": {
"title": "name",
"released": "release_year"
}
NOTE: In case you want to migrate a different dataset (other than the movies dataset) you can extract the current neo4j ontology into a configuration file using the following command:
python3 neo4j_to_csv_extractor.py --password <your-neo4j-password> --generate-template <your-template>.json --analyze-only
When ready, execute export script (where migrate_config.json is holding the movies dataset ontology with optional labels mapping):
python3 neo4j_to_csv_extractor.py --password <your-neo4j-password> --config migrate_config.json
You can see sample output of the script in the GitHub repo.
Nodes and Edges files are created in the csv_output sub-folder.
Step 3: Install and Run FalkorDB
Next, install and run the FalkorDB graph database according to https://docs.falkordb.com/getting_started.html
The following command runs FalkorDB and its integrated browser on the local machine:
docker run -p 6379:6379 -p 3000:3000 -it falkordb/falkordb:edge
You are now ready to go to http://localhost:300 to see the FalkorDB Browser.
Step 4: Loading CSV Files into FalkorDB
Now is the time to load the data to FalkorDB:
python3 falkordb_csv_loader.py MOVIES --port 6379 --stats
As you can see FalkorDB supports multiple graphs, so you need to indicate the graph name, in this case, MOVIES.
NOTE: In case your FalkorDB instance data plane is secured, you can add username and/or password as mentioned in github.com/FalkorDB/Neo4j-to-FalkorDB
Step 5: Validate the Import
Using the same redis-cli, you can verify the graph with the following queries:
GRAPH.QUERY MOVIES "MATCH (n) RETURN COUNT(n)"
GRAPH.QUERY MOVIES "MATCH ()-[r]->() RETURN COUNT(r)"
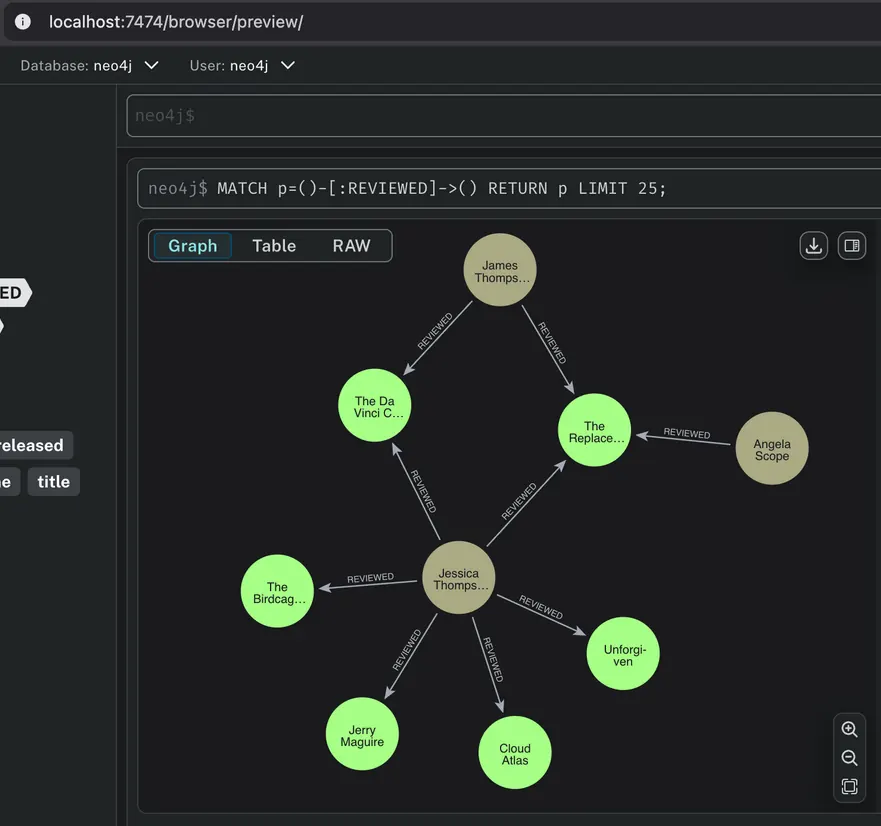
An example of a Cypher query and how neo4j and FalkorDB browsers visualize the data is shown below (using the ‘movies’ dataset as reference):
Neo4j Browser
FalkorDB Browser
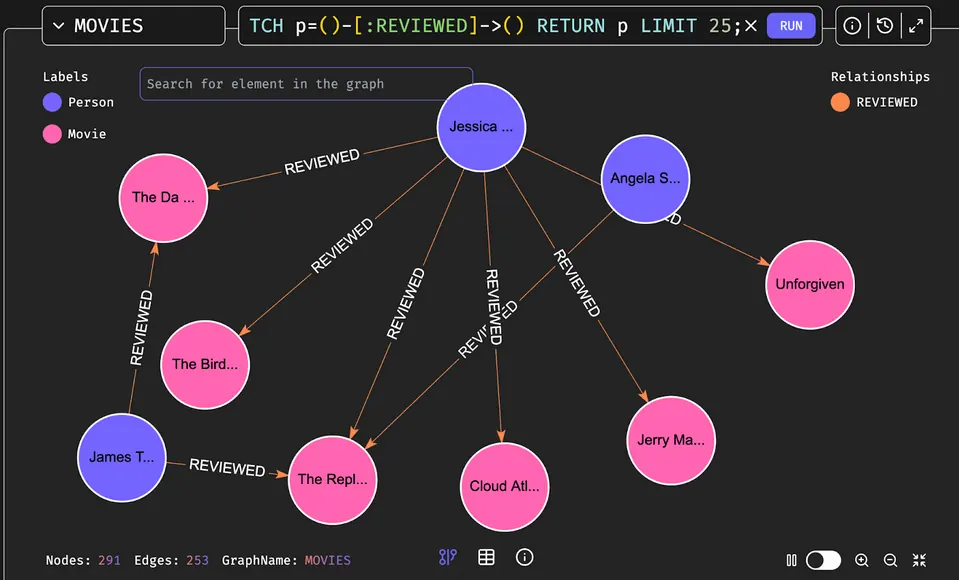
MATCH p=()-[:REVIEWED]->() RETURN p LIMIT 25;
Next Steps
After migrating from Neo4j to FalkorDB, it is recommended to compare sample queries to verify data accuracy. Once you are confident in the accuracy of the results, update your application to connect to FalkorDB.
For large graph sizes exceeding a single server’s memory capacity, contact the FalkorDB team for guidance on reducing the memory footprint. Optimization options include:
- Conducting an architectural review for more efficient data modeling.
- Dividing the graph into smaller sub-graphs.
- Using memory optimization techniques, such as string interning to reduce redundancy (e.g., assigning a card suit attribute).
For example, you can use the following query to implement string interning:
MERGE (s7:card {card_suit: intern('spade')})
After completing the migration, leverage FalkorDB’s integrations with GenAI frameworks like GraphRAG-SDK, Graphiti, LlamaIndex, and LangChain to build accurate, scalable GraphRAG applications.
To get started, visit the FalkorDB website for comprehensive documentation, to download the latest version, or to sign up for FalkorDB Cloud.
Citations & sources
1. FalkorDB. (2025). FalkorDB vs Neo4j: Choosing the Right Graph Database for AI.
2. FalkorDB. (2025). FalkorDB vs Neo4j: Graph Database Performance Benchmarks. https://benchmarks.falkordb.com
Neo4j owns all Neo4j-related trademarks, service marks, and logos (c)